When we are talking about tube bending, we should speak also about the next stage of the production—the tube measurement. This procedure confirms that the tube is bent correctly and fits the requirements.
Why is it interesting to speak about the measurement? Because the part (tube after bending) is not the linear part, and the market offers a completely other solution to use in tube measurement.
Measurement or verification is not the subject of our business, but anyway we need to know about it and how it is done and provide the consultancy assistance if required.
Main idea
The tubes after bending are divided into 2 big categories. First, if the tube itself is the final part or one of the main parts of the construction. In this category we are talking about handles, rails, supports, legs, etc. And one of the important points—this is not the tube for any liquid or gas. We are talking about all transport handles, handles for different devices (lawnmower handle, bike or bicycle handle, etc.), tubes for furniture, parts for architecture, and so on.
In the second category, the tube is part of the big system and used for transportation of the liquids (hydraulic oil, various gases, water, etc.), for example, hydraulic systems. The more complicated the system, the more tubes are inside, and they are bent in a way to prevent collisions with other parts and places of the entire system. This is where measurement became extremely important to verify that the bent tubes were really fabricated in a way that does not allow any collision with other pieces.
In the first category, factories are usually interested in measuring the complete part to ensure that it is the same as in the project or design.
In the second category it is much more important to verify and measure critical areas of the tube (risks for collision) to approve that the tube could be installed in the system.
Digitization
Thanks to modern technologies, the measurement is performed in the digital environment, which means that the digital model of the tube could be compared to the real one with the indication of all main differences found. The user can define the most important places and surfaces for the optimal result.
Also, the modern tube bending machines can get the information directly as the feedback from the measuring system for approval of the bending program or importing of correction values to adjust the result according to the requirement values.
The digital environment provides more precise action of measurement, and also additional elements could be controlled, such as presenting on the tube of nipples, rings, formings, brackets, etc.
The measurement in digital can provide one more possibility: prepare the geometry of the unknown tubes when production doesn’t want the control and verification of the tube already known but the measurement of the unknown tube or reverse-engineering.
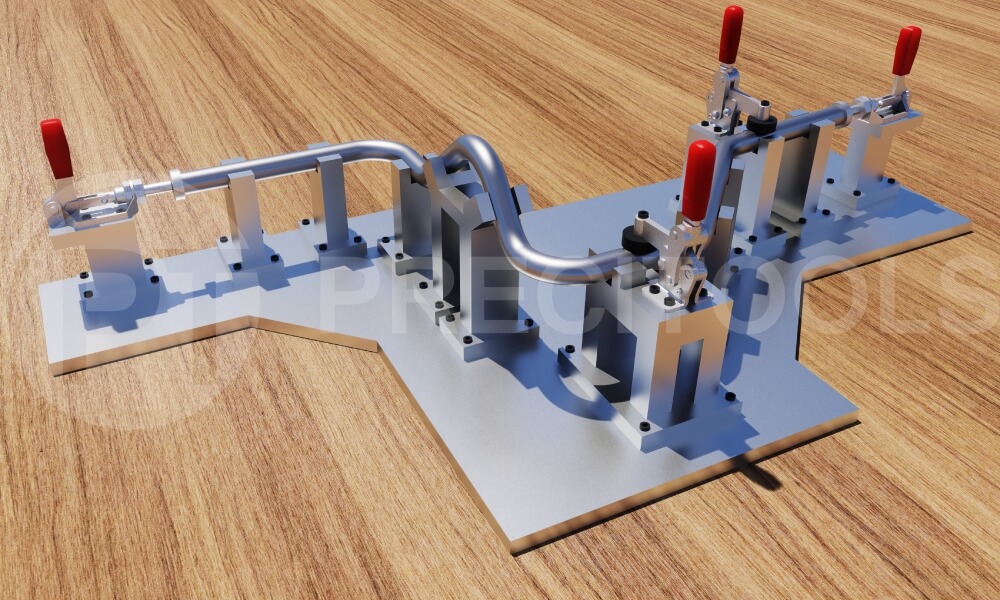
Jigs or fixtures
Jigs or fixtures are the most general and typical method for control of tubes after the bending. They have a lot of advantages—no additional operation of measurement devices, no requirements for high skills of workers, and they are very fast and very effective.
Fixtures are made to control the tube in the most important places (the risks of collisions) and complete the fitting of the geometry. Thanks to the digital interface, the projecting of the fixtures now is much easier—they can be made in a digital environment based on a tube model and then transferred to real parts to prepare the construction.
But this way has disadvantages as well—in particular, the big quantity and different types of tubes lead to the necessity to prepare a lot of different fixtures for all of them. Also, as the measuring device, jigs or fixtures should also be verified, one time per several years probably.
Contact measurement
First, it is important to say that the mechanical gauges, instruments, and tooling are nearly useless for the measurement of bent tubes in case the tube was bent in a 3-dimensional way. If it was bent in one plane, it is possible to use classical instruments, for example, mainly gauges for control of the angle and main linear dimensions.
Contact measurement with a touch probe is one of the measuring types that can be used in separate devices or a coordinate measuring machine (CMM). Based on points of contact that the software creates, the geometry of the surface, and based on this geometry, it is possible to generate the centerline of the tube and the main direction. Absolutely sure that all possibilities are based on the possible software. Probably also contact measurement is the only possible way to measure really big tubes that cannot be positioned into any machine or device. With good software this type of measurement can provide the most precise results.
In theory, a coordinate measurement machine could be a universal machine to be used for control of tubes as well if necessary (based on the specifications and limits) but mainly used for other parts.
The modern market also offers the mixing of different technologies of measurement—the use of mobile or handy contact probes with the reading of the position of it by visual technologies to provide the effective and universal solution.
Non-contact measurement
Modern technologies provide the technologies of non-contact measurement with the use of laser devices (generally laser forks for articulated arms) and visual and optical technologies with the use of photogrammetry. Such ways measure the tube geometry based on the known length of primary measured markers or spots. Probably this technology is less accurate than contact measurement but makes the process much faster without the necessity of positioning the probe.
As with contact measurement, the efficiency of such technologies and devices is based on software possibilities and integration.
For both technologies, non-contact and contact measurement, the advantages are the absence of fixtures and jigs for each tube and the necessity of storage.
Also, non-contact measurement is the future, which is basically also used in robotic vision, so it could be used for any automation of production and use of automatic devices such as robots or transferring devices.
Absolutely sure this is the most modern technology and will be developed to increase the precision, possibilities, and time of scanning.
In the meantime, fixtures and jigs will stay in the production forever because this is the cheapest and most effective solution with big quantities, but just several models of tubes, like the massive production of exhaust pipes for a specific model of automobile.